Gain and Read Noise
The conversion gain of the camera and the readnoise
was measured by the following procedure:
- A series of pairs of exposures using the
Fowler method of a
uniform light source were made with different
exposure times.
- The mean signal level
of the frame above bias level
- Frames with identical exposures were subtracted and the
variance was calculated.
The variance was then divided by two
to give the single frame variance.
- A linear fit made to the result
Note: outliers outside of 5 sigma in the difference images were
rejected to calculate the variance.
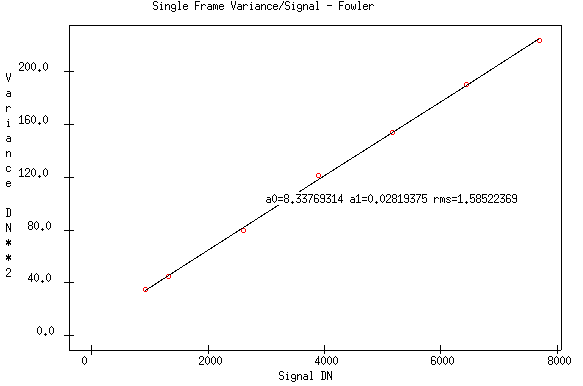
- Gain: 35.7 e-/DN
- Noise: 103 e- r.m.s.
Note: This value differs from the value of 30 derived
for the
Mark I camera
by more than the expected errors.
I do not know the reasonf for this discrepancy as the
electronics have not been changed.
Gain Discussion
We can convert the conversion gain into the signal by following
the signal chain which has the following characteristics:
- preamplifier gain: 5.1
- ADC conversion 10 volts range for 16 bits
- 30 µ V at output FET per DN
Hence 1 e- corresponds to about 1 microvolt.
This is a factor of
two lower than mean value of the range (1.5 - 2.5 µ V/e -)
quoted on the
Rockwell
Specification Sheet.
I don't know if this indicates some problem in the measurement,however,
there are other reasons to be suspicious of this value.
Noise Discussion
The noise resulting from the difference of two Fowler frames is
pretty white as the next image shows.

Last Revised November 2, 2000


